
DONE WITHIN A CLICK: HOW SMART CONTRACTS ARE RESHAPING THE FINANCE INDUSTRY
Some 10 years ago the idea of signing a contract without paper and pen was unthinkable – today thousands of businesses leverage the potential of blockchain-powered self-executing agreements. The finance industry seems to be one of the prime beneficiaries of the technology, so let’s dig into the essence of decentralized smart contracts and see how they are changing the game rules.
Smart contracts explained on the fingers
Simply put, a smart contract is a self-executing program that runs on a blockchain network, automating the process of verifying, enforcing, and executing the terms of a contract. Think of it as a digital agreement that is automatically carried out once certain predefined conditions are met. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers or brokers, and enables direct, secure, and transparent interactions between parties. The term “smart contracts” was coined by computer scientist Nick Szabo in 1993. Inspired by other researchers, Szabo believed that the development of smart contracts through cryptographic protocols and other digital security mechanisms could significantly improve the execution of traditional contracts.
What lies behind a click-to-sign?

Before integrating the technology into your workflow, it’s vital to understand its essence. Smart contracts are digital agreements that work on an “if/when…then…” statement basis. A simplified explanation of the concept looks like this:
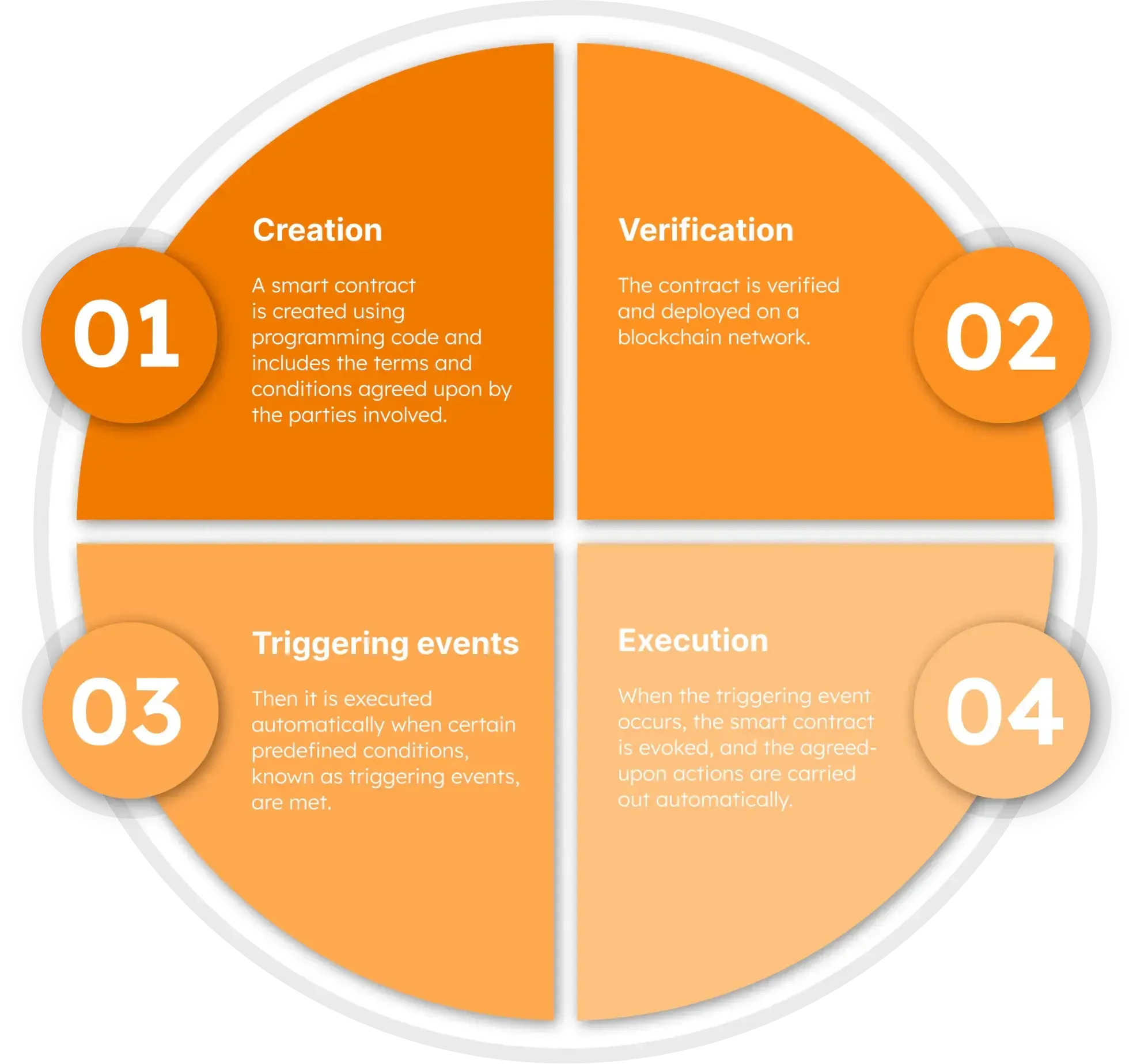

TRANSPERENCY: The beauty of smart contracts lies in their transparency as all parties involved can view the contract's terms, actions, and outcomes.

IMMUTABILITY: Once a smart contract is executed, it becomes part of the blockchain's permanent record. It cannot be altered or tampered with, ensuring the reliability of the transaction history.
How to create a smart contract?
Smart contract development is one of the most widespread requests our financial technology experts have been receiving recently. Given the momentum the technology is gaining, all sorts of financial institutions will be seeking trusted fintech software providers to create the new type of contracts to offer their businesses a secure, transparent, and efficient way to execute agreements. Here are the general steps involved in creating a smart contract:
Choosing the blockchain platform:
The first step in creating a smart contract is to choose the blockchain platform to develop it on. So far, Ethereum is the most popular one for this purpose.
Installation of the required tools:
Once the platform is chosen, the required tools to develop and deploy smart contracts are to be installed. For Ethereum, they are Truffle, Remix, MetaMask, and etc.
Choosing a programming language:
Smart contracts are typically written in programming languages like Solidity or Vyper. The choice is based on the compatibility with the previously selected blockchain platform.
Defining the rules and logic of a contract:
After choosing the programming language, smart contract developers define the contract’s logic, which includes specifying the functions and variables that will be used in the agreement.
Code writing:
Based on the contract definition, engineers will write the code for the agreement, which involves defining the rules and conditions for how it will behave and developing the logic for the functions.
Contract testing:
Once the code is written, it’s crucial to test the smart contract to ensure that it works as expected. Tools like Truffle and Remix are used to verify the contract and identify any inefficiencies.
Contract deployment:
After testing, a smart contract is deployed on a blockchain platform. There are several platforms available, and you’ll need to pay a transaction fee in cryptocurrency to deploy the contract.
Interaction with the contract:
Once the contract is deployed, you can interact with it using a Web3 interface like MetaMask.This allows you to send transactions to the agreement and execute its functions. You can also track the contract’s activity on the blockchain.
The list of steps is a long one but if you opt for a reliable fintech development team, there will be no need to get into the maze of smart contract building yourself, so choose wisely.
A magic wand for the finance industry

The potential of smart contracts goes far beyond finance but the widest application the technology has found within this particular domain, so let’s dive right into it and see what particular solutions it offers.
Automated payments
Smart contracts automate payment processes, ensuring timely and accurate transactions. For example, in insurance, claims can be processed automatically and payments released based on predefined conditions, reducing administrative overhead, improving customer satisfaction, and securing financial transactions.
Trade settlement
Streamlining trade settlement processes by automating the transfer of ownership and funds once specific conditions are met are within the power of self-executed contracts. They eliminate the need for intermediaries and reduce settlement times, making transactions more time- and cost-effective.
Loan agreements
Automation of loan agreement management, including repayment terms, interest calculations, and collateral management is a major task smart contracts can accomplish with ease. Their implementation reduces the risk of human error and provides transparency to both lenders and borrowers, enhancing trust and efficiency of lending processes.
Supply chain finance
Smart contracts are able to facilitate supply chain finance by enabling self-operating payment terms and ensuring timely settlements between buyers, suppliers, and financiers. This improves cash flow management, reduces transaction costs, and strengthens relationships within the supply chain ecosystem.
Derivatives and options
The use of complex derivative instruments, such as options or swaps, can also be streamlined using the technology to eliminate the need for intermediaries and reduce counterparty risk. This increases efficiency, enhances transparency, and enables real-time settlement of derivative contracts.
Regulatory compliance
Smart contracts are helping businesses comply with regulatory requirements by observing and executing compliance processes. For instance, by embedding compliance rules within smart contracts, companies can ensure adherence to Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules, and other compliance frameworks.
Crowdfunding and ICOs
Last but not least, blockchain-based contracts have transformed the crowdfunding landscape by enabling Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). These agreements automatically distribute digital tokens to investors and establish predefined rules for token transfers, dividend distribution, and governance, providing transparency and security to all participants.
Wrapping up
Smart contract development has breathed new life into every facet of finance. To date, it is a rare financial company that goes without integrating the industry-leading fintech solution into its workflow. As the need for self-executing agreement building grows, the question of finding a dedicated and skilled team of fintech enthusiasts remains. Opt for no less than senior-level domain experts as tailored fintech software solution development requires much more than a simple one-fits-all approach.